ASTM E2149 : 2020 – Standard Test Method for Determining the Antimicrobial Activity of Immobilized Antimicrobial Agents under Dynamic Contact Conditions
ASTM E2149 test quantitatively evaluates the effectiveness of samples treated with non-leaching antimicrobial agents under dynamic contact conditions. ASTM E2149 is also referred to as “dynamic shake flask test”.
Immobilized antimicrobial agents, such as surface bonded materials, are not free to diffuse into their environment under normal conditions of use. ASTM E2149 test ensures good contact between bacteria and the treated sample by constant agitation of the test specimen in a bacterial suspension during the test period (1 hour).
Products that can be tested with ASTM E2149 Test
ASTM E2149 test is applicable to measure the antimicrobial activity of non-leaching (immobilized and not water-soluble), irregularly shaped, or hydrophobic surfaces. The products tested with the ASTM E2149 include fabric, paper, powder, granular material and other solids.
Preparations for ASTM E2149 Test
- Bacterial Inoculum – Log phase test bacterial inoculum (18 hours old culture) is taken for performing this test. The working test bacterial inoculum of a known titre is prepared by diluting the log phase stock with sterile buffer solution
- Test specimens – Each treated and untreated specimen should be 0.5 g -2 g. The size of the specimen material is selected on the basis of weight.
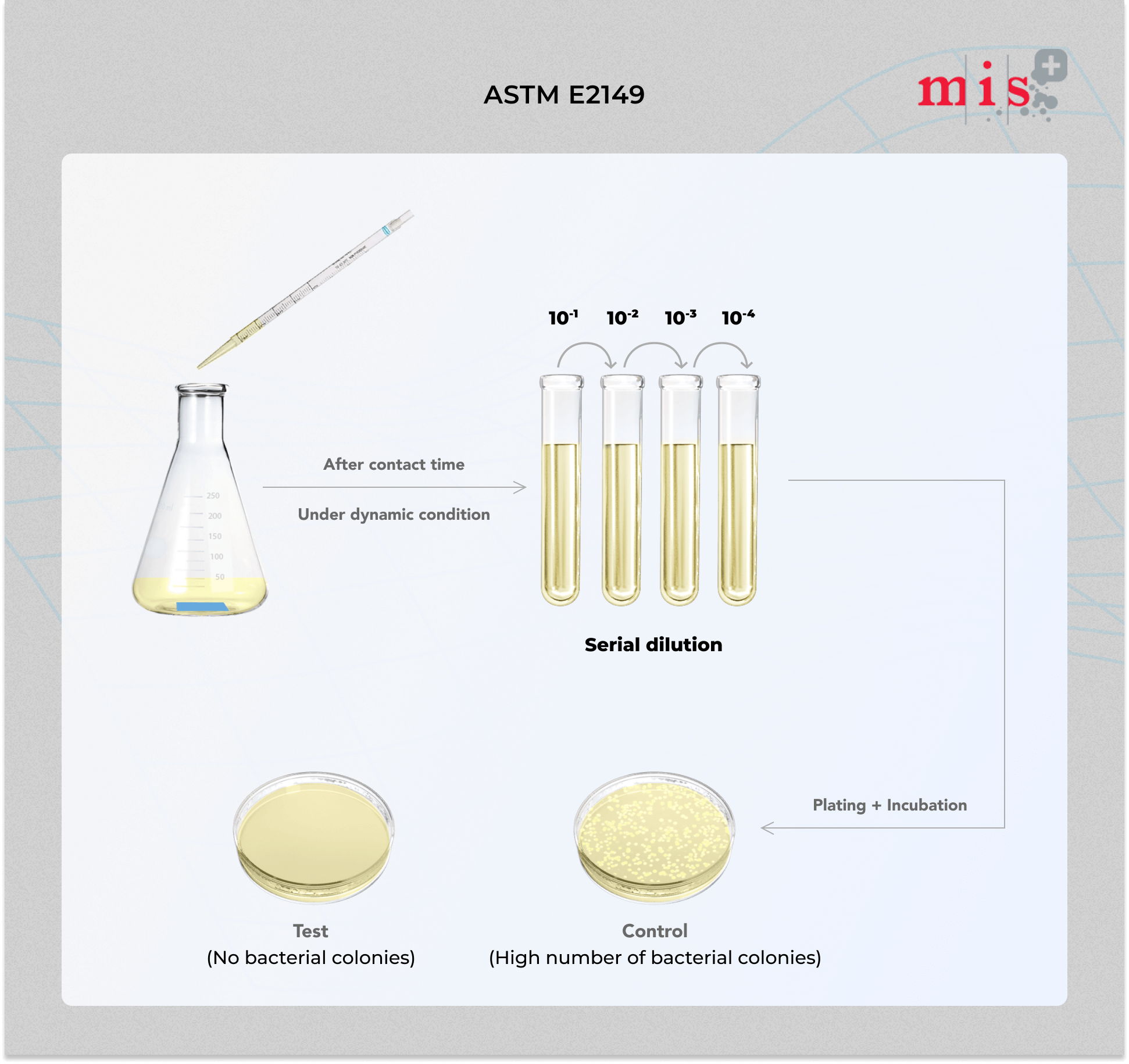
ASTM E2149 Test Procedure
1. ASTM E2149 test method is designed to evaluate the resistance of specimens treated with a non-leaching antimicrobial agent by shaking in a microbial suspension.
2. Both antimicrobial treated and untreated specimens of each testing material is required.
3. These specimens are kept separately in 250 mL screw-cap Erlenmeyer flasks and working bacterial dilution is added to them.
4. All the specimens are shaken in dynamic shake flasks in a wrist action shaker to ensure good contact between the bacteria and the treated fibre, fabric, or other substrate by constant agitation of the test specimen in a bacterial suspension during the test period.
5. Microbial concentrations in the treated and untreated specimens are usually determined at 0, 1 or 24 hours contact time.
You can connect with our experts to discuss your requirements for the ASTM E2149 test today. Our specialist consultants are at the forefront of developing high-performance testing services, from understanding the customer’s needs to assisting the desired outcomes. We will be happy to assist you.
FAQs
The ASTM E2149 is used for ‘Determining the Antimicrobial Activity of Immobilized Antimicrobial Agents Under Dynamic Contact Conditions’ is a sensitive test, often used to measure the antimicrobial activity of non-leaching, irregularly shaped or hydrophobic surfaces.
ASTM E2149 test is applicable to measure the antimicrobial activity of non-leaching (immobilized and not water-soluble), irregularly shaped, or hydrophobic surfaces. The products tested with the ASTM E2149 includes fabric, paper, powder, granular material and other solids.
The ASTM E2149 test takes 3 to 4 days.
At Microbe Investigations, we understand the need for accuracy and speed. We test for the ASTM E2149 using the following microrganisms: Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 15442), Escherichia coli (ATCC 8739), Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538P), Enterococcus hirae (ATCC 10541), Klebsiella pneumoniae (ATCC 4352), MRSA (ATCC 33591), Salmonella enterica (ATCC 10708), Candida Albicans (MTCC 3017). Additional strains can be added on request.
Contact us for more information
Explore Other Tests
ASTME2149 | AATCC-100 | JISZ2801 | JISL1902 | EN 1276 | ISO 22196 | ISO 20743 | ISO 846 | ASTM E2180 | AATCC 147 | ASTM D7907-14 | ASTM E3031 | ASTM G29 | EN 16615 | EN 13697 | PAS 2424 | EN 1040 | EN 14349 | EN 13727 | EN 14561 | ASTM G22 | ASTM E1153 | ASTM D2574 | AATCC 174 | EN 14563 | EN 13704 | EN 1499 | EN 1500 | EN 14347 | EN 14348 | EN 1656 | EN 16437 | EN 12791 | ASTM E1174 | ASTM E2362
Antifungal Testing
AATCC 30 | ASTM G21 | EN 1650 | EN 1657 | EN 13624 | EN 1275 | ASTM C1338 | ASTM D5590






